New Recommendations to Make IUD Insertion Less Painful
There is new guidance on pain management for IUD insertion and acknowledgement that providers often underestimate the pain patients feel during their procedures.
Molluscum:
Fast Facts
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) may be sexually transmitted by skin-to-skin contact (does not have to be mucous membranes) and/or lesions. Transmission through sexual contact is the most common form of transmission for adults.
MCV may be passed on from inanimate objects, like towels or clothing that come in contact with the lesions. MCV transmission has been associated with swimming pools and sharing baths with an infected person.
MCV also may be transmitted by autoinoculation, such as touching a lesion and then touching another part of the body. To stop from further spreading the infection, do not shave over or close to areas that are visibly infected.
The time between when a person is infected and when they begin to show symptoms is called the incubation period. For molluscum, the incubation period averages two to three months, but it may range from one week to six months. So someone may see symptoms in as little as a week, others may take as long as six months. On average, it takes two to three months.
Diagnosis is usually made by the characteristic appearance of the lesion, so a provider can often tell by just looking. A provider can also take a specimen from the lesion and view it under a microscope to confirm.
The most common complication from molluscum is a secondary infection caused by bacteria. This can be more of a problem for people with compromised immune systems.
Because transmission through sexual contact is the most common form of transmission for adults, preventing skin-to-skin contact with an infected partner will be most effective in preventing MCV.
Condoms or other barriers for vaginal, oral, and anal sex may help to prevent such contact. Using spermicides is not recommended as they can irritate the skin or vaginal tissue and, especially for women, cause abrasions (tiny openings in skin) that may make it easier to contract sexually transmitted infections.
If you do get molluscum contagiosum, avoid touching the lesion and then touching another part of the body without washing your hands to prevent any chance of spreading the infection.

There is new guidance on pain management for IUD insertion and acknowledgement that providers often underestimate the pain patients feel during their procedures.

The FDA just approved a new, fully at-home test for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis. The tests, which is only for women, will be available without a prescription. Users can collect their own sample and have results in less than 30 minutes.
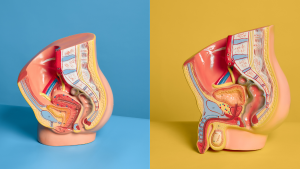
Our reproductive health is an important part of our sexual health and our overall health. It includes our reproductive organs and our ability to get pregnant or get someone pregnant when we choose.

Anyone who is having penis-in-vagina sex runs the risk of getting pregnant every time they have sex. Even if it’s your first time. Even if you have your period. Even if it’s a full moon and Mercury is in retrograde.

A new study found that opt-out screenings for all patients in emergency departments caught numerous cases of syphilis and HIV that would have gone undetected under other screening protocols.

A study revealed that the majority of young people would prefer testing for STIs at home over going to a doctor’s office or clinic.

Many STIs have no signs or symptoms in the majority of people infected. The only way to know if you have an STI is to get tested.

LARC methods are safe, reliable, and prevent pregnancy for years. For many people they are a great choice, but everyone has personal preferences for what fits in to their lifestyle and health profile.
ASHA believes that all people have the right to the information and services that will help them to have optimum sexual health. We envision a time when stigma is no longer associated with sexual health and our nation is united in its belief that sexuality is a normal, healthy, and positive aspect of human life.
ABOUT
GET INVOLVED
ASHA WEBSITES
GET HELP
© 2025 American Sexual Health Association